Resonac’s Patent on Magnetic Molding Compound for Inductors Upheld
- The product contributes to better reliability and magnetic properties in inductors for ADAS, memory modules, and smartphones -
February 08, 2024
Resonac Holdings Corporation
Resonac Corporation (President: Hidehito Takahashi, hereinafter "Resonac") is pleased to announce that our Japanese patent (Patent No. 7081612) on magnetic molding compound for inductors*, which was opposed by a third party, was judged to be valid by the Patent Office on November 2, 2023.
In recent years, technologies such as AI (artificial intelligence), IoT (Internet of Things), 5G (5th generation mobile communication systems), and ADAS (advanced driver assistance systems) have become more widely available, requiring more complex controls in all devices, from smartphones to xEVs (electric vehicles). This has led to an increase in demand for inductors, which are needed for signal noise reduction and voltage control.
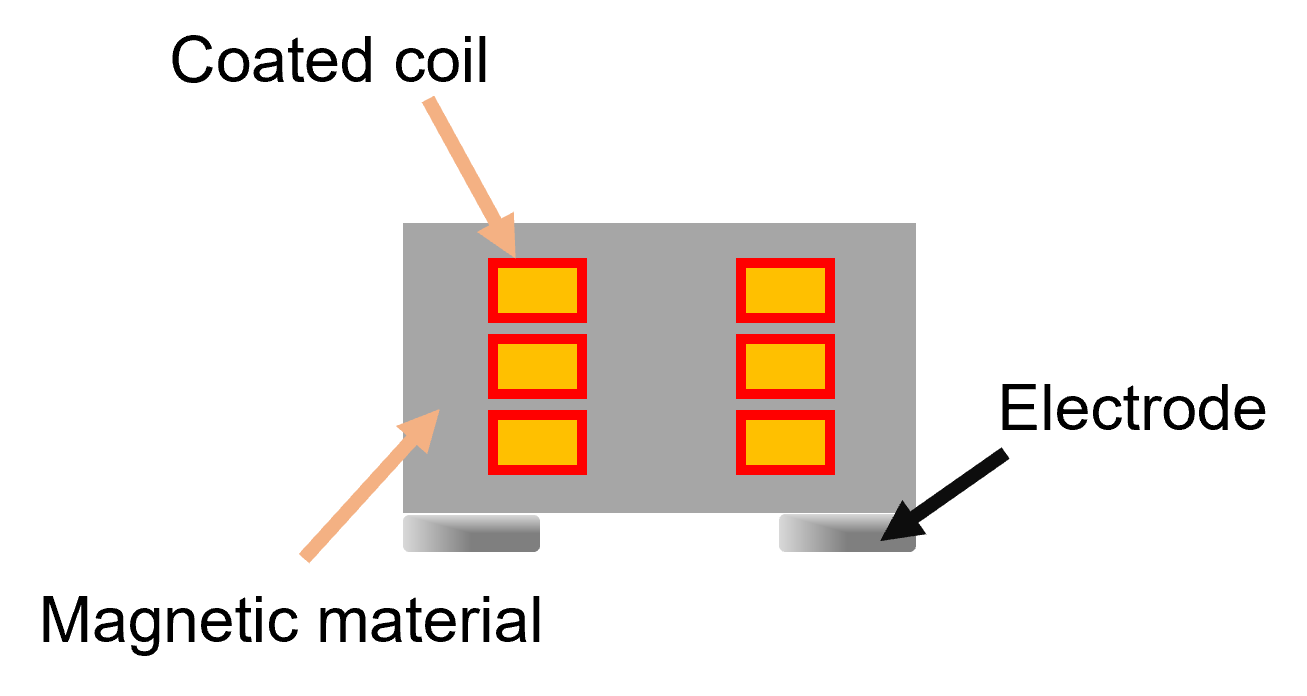
Inductors used in power supply circuits are mainly wire-wound inductors, where the conductor is wound in the form of a coil. Wire-wound inductor is manufactured by molding its windings with magnetic material consisting of a mixture of resin and magnetic powder, and this is usually compressed under high pressure to improve the inductor’s magnetic properties. However, there are risks of coil deformation, winding collapse, and cracks that can be caused by this pressure, which can ultimately result in reduced reliability. To counter these issues, we have developed—by improving the types and mix of resin and magnetic powder included in the magnetic material—a proprietary magnetic molding compound for inductors which can be molded under low pressure and yet improve magnetic properties. Mass production of this molding compound began in 2020. These products are primarily used in power inductors for ADAS, memory modules, and smartphones, contributing to the reliability and magnetic properties of these devices. Recently, we have also been considering expansion into semiconductor applications.

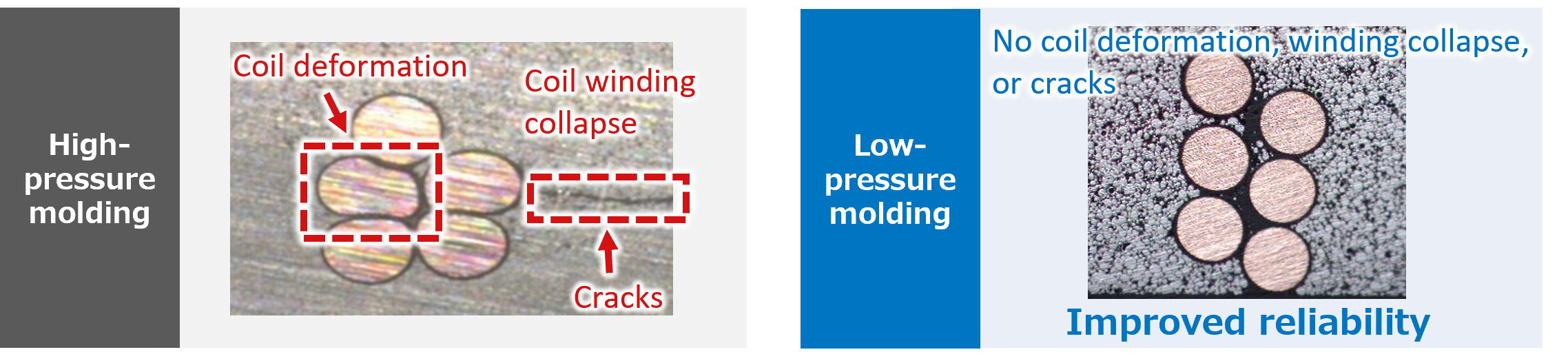
In 2022, Resonac was granted a patent for our magnetic molding compound for inductors. However, in November 2022, a third party filed an opposition to our patent, and we later received a notice of reasons for revocation of the patent from the Patent Office. In response, we made partial corrections and submitted a request for correction and a written opinion to the Patent Office. Our response was accepted after being considered by the Patent Office and the decision was recently made to uphold our patent.
The technology in this patent has also been patented in the U.S. and China, and is under examination in Europe.
We are continuously applying for Japanese and international patents for inventions in the area of magnetic molding compound technologies for inductors, and are working to build a strong portfolio of patents.
We will continue to apply for and obtain patents in line with our business strategy, and promote healthy competition and enhance the value of our technologies by legally protecting our intellectual property rights.
* An inductor is a passive element (electronic component) with a conductor wound in the form of a coil. Inductors come in wire-wound, thin-film, and multilayer types, and they are further categorized into two types: inductors for high-frequency circuits that select high/low-frequency signals and eliminate signal noise, and inductors for power supply circuits (power inductors) for voltage control.
For further information, contact
Public Relations Group, Brand Communication Department
